Introduction to Google NoteBookLM
Google NotebookLM is a free tool that leverages AI and a technique called retrieval augmented generation (RAG) to help users understand and work with their documents.
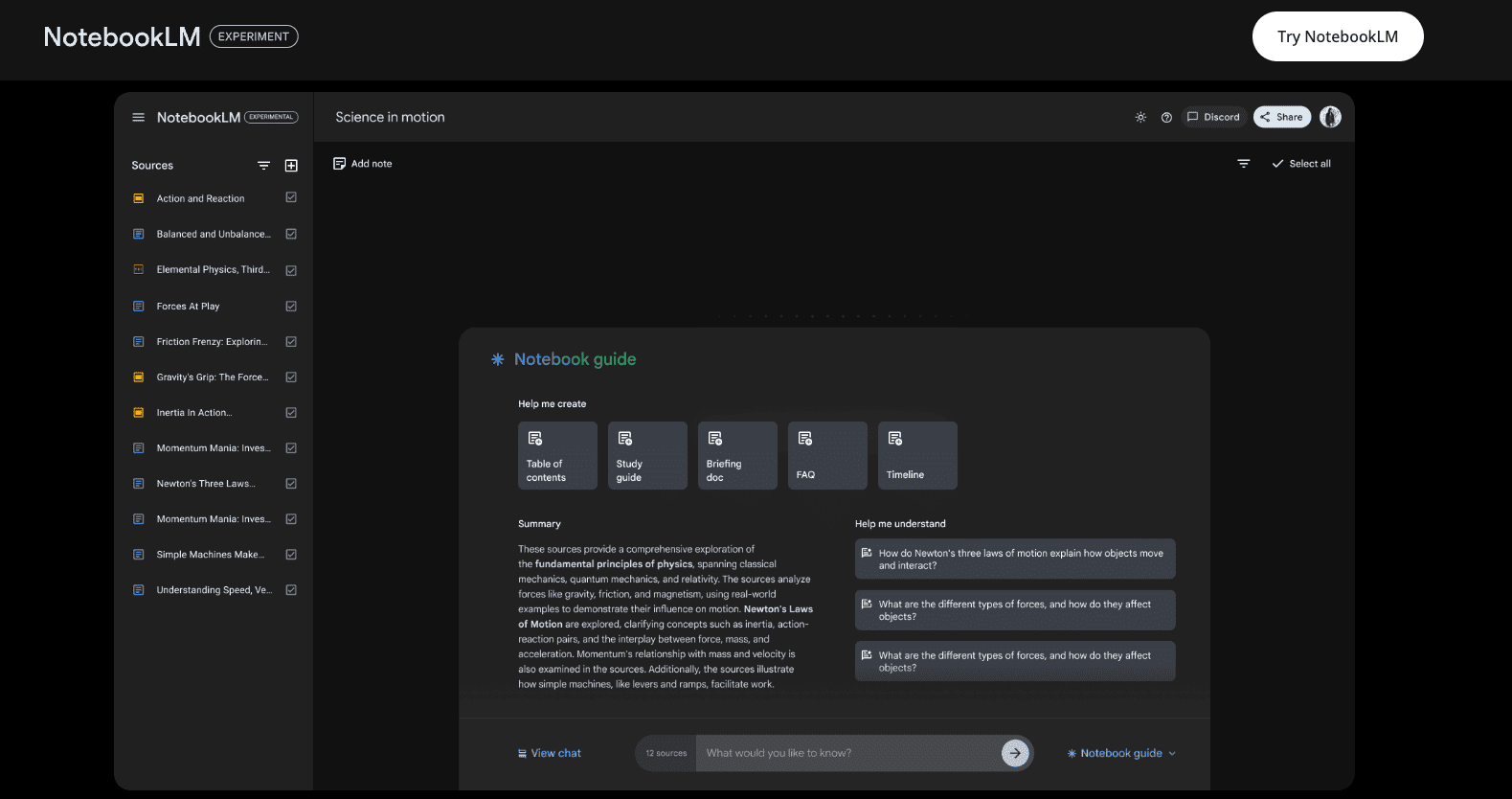
Google NoteBook LM – Functionality and Features
Document Processing and Analysis
Users can upload various source documents including PDFs, text files, markdown files, Google Docs, and Google Slides. NotebookLM processes these documents and uses AI to understand their contents.
Information Extraction and Question Answering
Users can then query their documents using natural language through a chatbot powered by the Gemini 1.5 Pro AI model. This enables them to extract specific information, get answers to their questions, generate summaries, create study guides, and even produce podcasts based on the documents.
Citation and Accuracy:
Crucially, NotebookLM provides citations for the information it presents, indicating precisely where the information originated in the source documents. This transparency ensures that the AI is not fabricating information (“hallucinating”) and allows users to verify the accuracy of the responses.
Workflow and Entities
- Notebooks: The platform revolves around the concept of “Notebooks,” serving as containers for organizing notes and source documents. Users can create multiple notebooks for different topics.
- Sources: Sources are the documents users upload to NotebookLM. The tool allows up to 50 sources per notebook, with each source having a limit of 500,000 words.
- Notes: Notes are created based on the user’s interaction with the sources. There are five ways to create notes: manually adding a new note; automatically generating a source overview (summary) and key topics upon source upload; saving answers from the chatbot; combining existing notes; and highlighting text within a source document to create a new note.
- Chat: The chat functionality is central to NotebookLM, enabling users to query their uploaded sources and notes using natural language. Currently, the chat history does not persist, meaning it is lost if the user refreshes the page.
Interface and User Experience
The NotebookLM interface is designed for intuitive interaction:
- Source Panel: Located on the left, this panel displays all uploaded sources. Users can manage their sources by renaming, deleting, adding more sources, or viewing the AI-generated summary and key topics for each source.
- Notebook Title and Settings: The top bar displays the notebook’s name, which can be edited. It also houses settings for sharing the notebook with collaborators, switching between light and dark modes, accessing help documentation, and joining the NotebookLM Discord server.
- Notes Panel: Situated to the right of the source panel, this section displays all the notes created within the notebook.
- Chat Box: Located at the bottom, this is where users type in their queries to interact with the AI.
- Note Guide: Accessible from a tab, this section provides a summary of all sources in the notebook, suggested questions for querying the sources, shortcuts to generate specific outputs (e.g., FAQs, study guides, table of contents), and the audio podcast generation feature.
Limitations and Considerations
- Experimental Stage: NotebookLM is still in its experimental phase, meaning users may encounter bugs, inconsistencies, or occasional “hallucinations” where the AI generates inaccurate information.
- Domain-Specific Knowledge: NotebookLM’s AI is trained on the user’s uploaded documents. It cannot answer general knowledge questions or provide information outside the scope of the provided sources.
- Chat History: As mentioned earlier, the current version of NotebookLM does not retain chat history, posing a potential inconvenience for users.
Google NotebookLM Key Features:
- AI-Powered Document Processing: NotebookLM leverages AI, specifically Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), to process and analyse uploaded documents, enabling it to act as a domain-specific expert.
- Document Compatibility: It supports various document types including PDFs, text files, Markdown files, Google Docs, Google Slides, website URLs, and even pasted text.
- Multi-Source Analysis: Users can upload up to 50 source documents, each containing up to 500,000 words, allowing analysis of large volumes of information.
- Information Retrieval: The tool can answer questions based on the information contained within the uploaded documents, providing citations for each answer.
- Content Generation: Users can generate various forms of content, including summaries, study guides, FAQs, tables of contents, and even podcast-style audio conversations based on the documents.
- Note-Taking Capabilities: NotebookLM offers five different ways to create notes: manually, from source document summaries, by combining existing notes, from chat outputs based on sources or notes, and by highlighting text within a source document.
- Multi-Lingual Support: The platform supports 35 languages, expanding its accessibility.
Google NotebookLM Benefits:
- Enhanced Understanding and Analysis: NotebookLM empowers users to understand and analyse documents more effectively by leveraging AI-driven insights.
- Time Savings: The tool streamlines content creation and research by automatically generating summaries, answering questions, and organising information.
- Increased Accuracy: Citations accompanying each answer ensure the information’s reliability and traceability within the source documents.
- Collaboration: NotebookLM allows for document sharing, similar to Google Docs, enabling collaborative work on projects like study guides.
Additional Insights
- Experimental Nature: NotebookLM is currently experimental, meaning users might encounter bugs or hallucinations.
- Data Privacy: Google assures users that uploaded data is never used for training purposes and remains private.
- Chat History Limitation: The current version doesn’t persist chat history; refreshing the page erases the conversation.
Google NotebookLM Conclusion
Google NotebookLM is a powerful tool for anyone looking to efficiently work with and extract information from their documents. Despite being in its experimental phase, it showcases the potential of AI and RAG in enhancing research, learning, and content creation. Future updates and refinements are expected to address existing limitations and further improve user experience.
